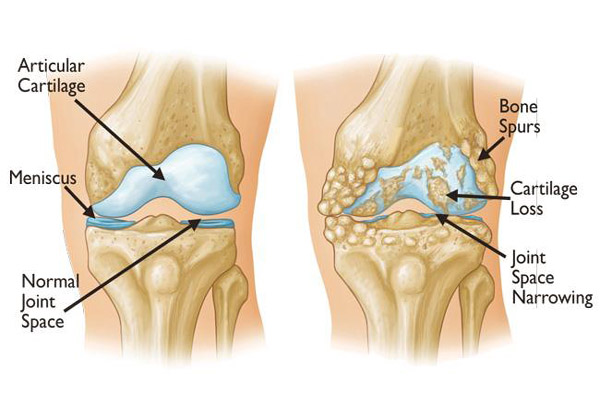
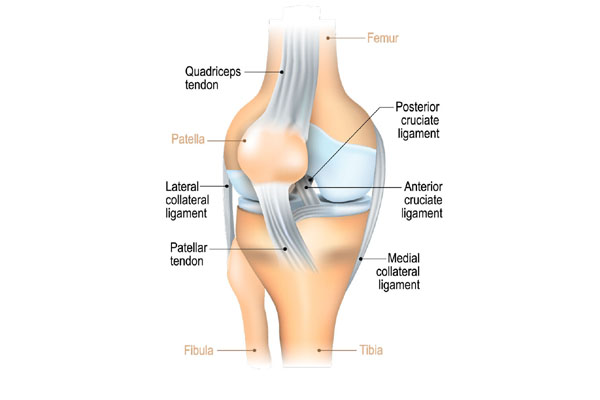
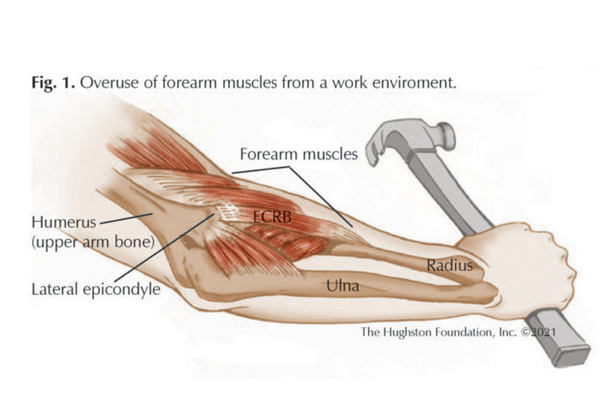
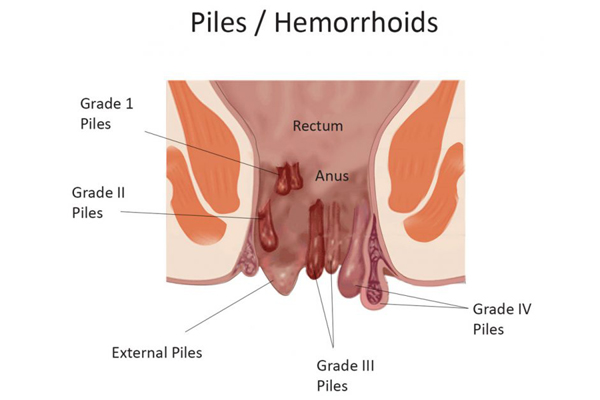
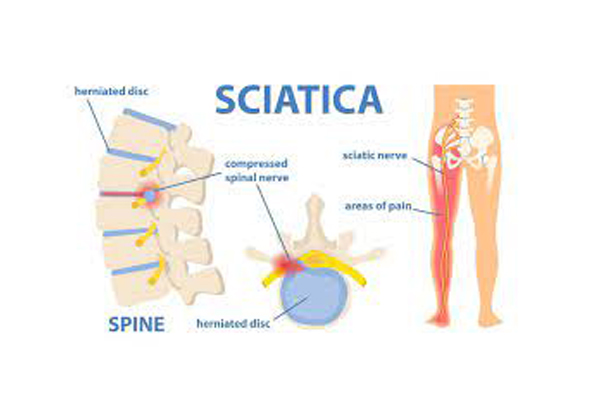
Arthritis is a joint disorder featuring inflammation. A joint is an area of the body where two bones meet. A joint functions to allow movement of the body parts it connects. Arthritis literally means inflammation of one or more joints. Arthritis is frequently accompanied by joint pain. Joint pain is referred to as arthralgia.
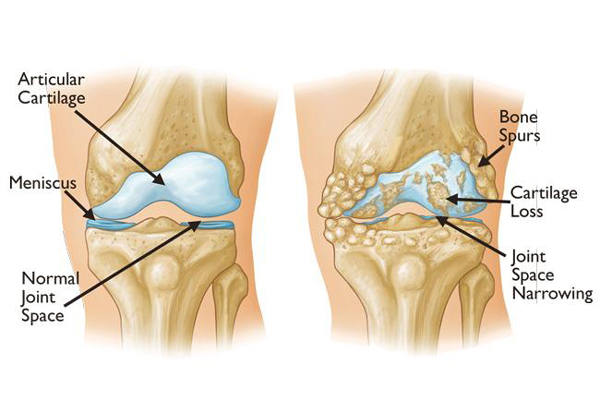
Arthritis is classified as one of the rheumatic diseases.they have a tendency to affect the joints, muscles, ligaments, cartilage, and tendons, and many have the potential to affect internal body areas as well.here are many forms of arthritis (over 100 have been described so far, and the number is growing). The forms range from those related to wear and tear of cartilage.rthritis sufferers include men and women, children and adults. More than half of those with arthritis are under 65 years of age.
SYMPTOMS of Arthritis:
- Inability to use the hand or walk
- Stiffness, which may be worse in the morning, or after use
- Malaise and fatigue
- Weight loss
- Poor sleep
- Muscle aches and pains
- Tenderness
- Difficulty moving the joint
- It is common in advanced arthritis for significant secondary changes to occur. For example, arthritic symptoms might make it difficult for a person to move around and/or exercise, which can lead to Secondary effects, such as: Muscle weakness, Loss of flexibility, Decreased aerobic fitness.